Simplified Guide to Understanding CEX & DEX
Imagine if you ordered a pair of shoes from your favourite online store and later discovered that they didn’t fit. You cry out in frustration to your friend because of how much the shoes cost, and your friend tells you she knows someone who could advertise your shoes and get a buyer, and you settle the person at a small price.
This is a bit about how cryptocurrency exchanges work.
What Are Cryptocurrency Exchanges?
Cryptocurrency exchanges are a type of organised market where different cryptocurrencies can be swapped or exchanged for either fiat currency or other cryptocurrencies.
This means if you have Bitcoin, you can exchange it for either a fiat currency like the dollar or another cryptocurrency like Solana or Ethereum.
Cryptocurrency Exchanges are quite popular, as it is almost only possible to trade cryptocurrencies with them. Very popular exchanges include; Binance, Bybit, Coinbase, Kraken, Kucoin, Crypto.com, etc. There are more than 500 cryptocurrency exchanges in the world.
Cryptocurrency Exchanges date back to 2009 after the invention of Bitcoin, where Bitcoin was sold through peer-to-peer trades on Bitcointalk, a forum for Bitcoin discussions at the time. Over time, there have been improvements in the services that cryptocurrency exchanges offer.
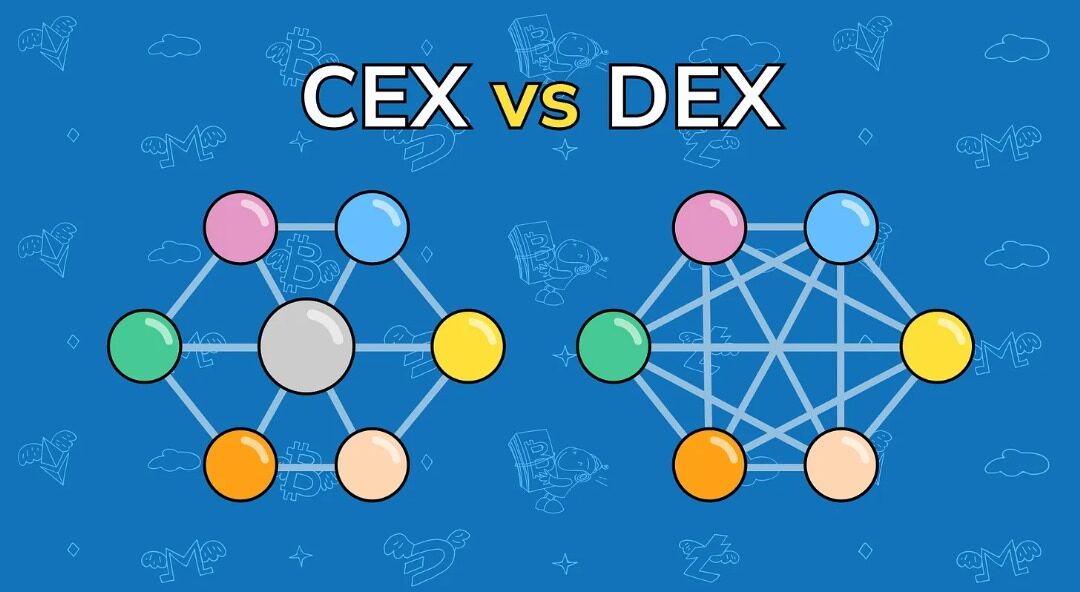
There are two main types of cryptocurrency exchanges, Centralised Exchanges (CEX) and Decentralised Exchanges (DEX). They both have different features, benefits and limitations which will be examined below, and help you make a decision on which you’d prefer for trading cryptocurrencies.
What are Centralised Exchanges (CEX)?
Centralised cryptocurrency exchanges are exchanges that act as a third party, and mediate transactions between buyers and sellers. They own the coins which are being traded and are under regulations.
Centralised Exchanges are quite popular and include; Binance, Bitstamp, Coinbase, Kucoin, Kraken etc.
To begin trading on a centralised exchange, you would have to do a know-your-customer (KYC) verification.
Advantages of Centralised Exchanges
- Centralised Exchanges are easy to use, secure and reliable. The KYC verifications help to identify customers and prevent criminal activities.
- Centralised Exchanges provide fair market pricing
- Unlike decentralised exchanges, you can exchange your crypto assets for both fiat and other cryptocurrencies
- They provide easy liquidity. This means that it is easy to buy and sell your coins because there are high volumes of transactions, making it easy to find a buyer or seller.
- They offer digital services such as margin or futures trading.
- They have digital wallets to help you store your cryptocurrencies, by holding your private keys.
Limitations of Centralised Exchanges
- Despite how easy and reliable CEX are, they are associated with high hacking risks. This is because the architecture of the exchange makes it vulnerable to cyber attacks and hacking just as any other software.
- You don’t have complete autonomy over your digital assets because the exchange manages your private keys, which give access to your digital wallets
- Centralised Exchanges are bound by many regulations in countries that limit your actions in trading. This also means that they are prone to sanctions by government institutions and the law.
- Higher transaction fees compared to decentralised exchanges
What are Decentralised Exchanges (DEX)?
Decentralised Exchanges are exchanges that don’t use any intermediaries or third parties in the trading of cryptocurrencies. It is founded on peer-to-peer transactions and uses smart contracts.
Smart contracts are coded programs that automatically execute when certain buying and selling conditions are met. It means that when buyers and sellers set their conditions if they match, they can be paired to trade.
Decentralised Exchanges are said to keep true to the main aim of cryptocurrencies in the first place, which is decentralisation, having no authority from banks and financial institutions.
Some decentralised exchanges include; Airswap, Uniswap, Pancakeswap, Venus, Sushiswap, dYdX, etc.
Advantages of Decentralised Exchanges
- There is no need for KYC verifications, and so users can stay completely anonymous.
- Complete control over your crypto assets as the exchange has no access to your private keys.
- Reduced hacking risks as the transactions occur between the digital wallets of the parties involved.
- Complete decentralisation as there are no points of control
- Wider access to more cryptocurrencies and digital assets
Disadvantages of Decentralised Exchanges
- Poor liquidity and low trading volumes: Liquidity is usually enhanced by backing cryptocurrencies with fiat currencies. This is unavailable in decentralised exchanges and so means it might be difficult to trade your crypto assets
- The interface is usually complex to use compared to CEX and errors could result in you losing your funds.
- High risk of scam coins: Decentralised Exchanges provide a wide array of coins and digital assets which means that scam and trick coins which can be easily rug-pulled can be present with no significant protection from the exchange
- Inability to trade with fiat currencies, since they are unavailable on the platform
With this knowledge of CEX and DEX, you can now choose which exchange platforms suit your preferences and start trading on your preferred exchange platform.
Stay in the know for all things Web3! Subscribe to our newsletter and become part of our vibrant community. Get exclusive updates and never miss any exciting developments.
Follow Us on All Platforms



